Updated on April 29, 2024
A Texas registered agent is a representative of a corporation upon whom any process, notice, or demand required or permitted by law can be served. The agent’s duty is to formally receive official documents and forward them to the corporation.[1] Every entity registered in Texas must continuously maintain a registered agent.[2]
Top Registered Agents (7)
| Company | Price ($) | Document Scanning | Agent Change Fee | Annual Renewal Fee | Mobile App? |
| *ZenBusiness 4.7 out of 5 – 13,467 reviews | $99/year | Yes | $0 | $0 | iOS | Android |
| Incfile 4.7 out of 5 – 15,944 reviews | $119/year | Yes | $0 | $0 | – |
| Harbor Compliance 4.0 out of 5 – 17 reviews | $99/year | Yes | $50 | $0 | – |
| Northwest Registered Agent 3.5 out of 5 – 62 reviews | $125/year | 15/year | $0 | $0 | – |
| Texan Registered Agent 2.9 out of 5 – 2 reviews | $50/year | Yes | $0 | $49 | – |
| InCorp Services 2.2 out of 5 – 16 reviews | $129/year | Yes | $0 | $49 | iOS |
| True Texas Registered Agent 0 reviews | $34/year | Yes | $0 | $0 | – |
*We collect affiliate fees from this company. Pricing is $99 for the first year and $199 for renewal.
Registered Agent Search
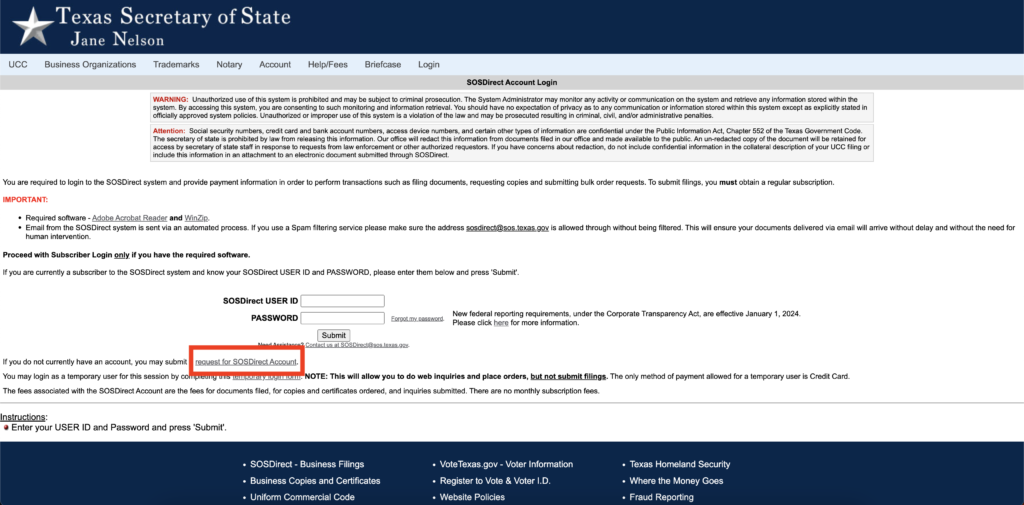
Step 1 – Visit the Secretary of State’s SOSDirect page. Click “enter site.”

Step 2 – Either enter your SOSDirect User ID and password and click “Submit” or click “request for SOSDirect Account” to sign up. Once logged in, search for an entity name and the registered agent associated. Each search costs $1.
Who can be a Registered Agent?
A registered agent can be an individual resident of Texas or a corporation authorized to do business in Texas. A corporation cannot be its own agent.[3]
The agent must have a physical address, which doubles as the entity’s registered office. The agent should be available at this address during normal business hours. A mailbox service or a telephone answering service is not sufficient.
Designating a Registered Agent
The most typical way for an entity to designate a registered agent is to include the agent’s name and address in its formation document.
To form an entity in Texas, select from the following forms. Complete the form, then send it, together with the filing fee, to the Secretary of State, P.O. Box 13697, Austin, TX 78711-3697.
- Domestic Corporation
- Form 201
- Filing fee: $300
- Domestic Nonprofit
- Form 202
- Filing fee: $25
- Domestic Limited Liability Company
- Form 205
- Filing fee: $300
- Domestic Limited Partnership
- Form 207
- Filing fee: $750
- Foreign Corporation
- Form 301
- Filing fee: $750
- Foreign Nonprofit
- Form 302
- Filing fee: $25
- Foreign Limited Liability Company
- Form 304
- Filing fee: $750
- Foreign Limited Partnership
- Form 306
- Filing fee: $750
- Foreign Limited Liability Partnership
- Form 307
- Filing fee: $200 per partner
Changing a Registered Agent
An entity can change its registered agent by filing a Statement of Change.[4] The agent must sign the statement to verify that the entity was informed of the change at least 10 days before filing.[5]
Once completed, the Statement of Change should be submitted to the Secretary of State, P.O. Box 13697, Austin, TX 78711-3697. The filing fee is $15.[6]
 Statement of Change
Statement of Change
Download: PDF
Resigning as a Registered Agent
A registered agent can resign by filing Form 402 with the Secretary of State. The statement must be filed before the 11th day after the entity is notified.
The resignation becomes effective 31 days after filing. Failing to maintain a registered agent continuously can put an entity at risk of being terminated, so it’s important that the entity files a Statement of Change (Form 401) after Form 402 is filed.
 Form 402
Form 402
Download: PDF